In the classic novel Gulliver's Travels by Jonathan Swift (1726), there is a silly debate between two groups of people on whether to break an egg through the wider end or the narrower end. These two groups of people are called big-endians and little-endians respectively.
Computing
In today's computing landscape, endianness refers to the ordering of the bytes in a piece of data. Big-endian is an order that places the most significant value in the byte sequence first at the lowest storage address. Big-endian data is easier for human to read as the bytes are positioned from left to right.
Little-endian on the other hand places the least significant value first at the lower storage address. Little-endian data are non-intuitive for human to read, but it is easier for computers to perform computations and hence improves efficiency.
Analogies and Examples
Here is a crude and simple analogy using the English sentence to represent in both big and little endian.
| Format | Sentence |
|---|---|
| Big-endian | I am going to the gym |
| Little-endian | gym the to going am I |
If you squint, it's basically reading the sentence from right to left for the sentence of little-endian.
A more realistic example is the representation of hexadecimal number.
| Format | Hexadecimal for | Full representation |
|---|---|---|
| Big-endian | 0x1234 | 0x12340000 |
| Little-endian | 0x3412 | 0x00003412 |
This online converter tool can be used to visualize different endianness from a hexadecimal string.
Little-endian Advantages
- Incremental processing
- Casts are no-op
- Backward compatible
- Ideal for devices with limited memory
- Faster arithmetic operations such as addition and subtraction
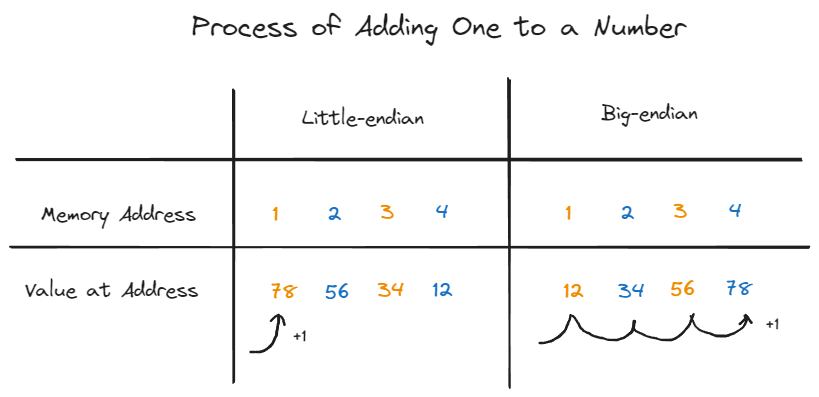
The process of adding one to the number above is easy for little-endian as the least significant byte is at the start of the memory address whereas for big-endian, it requires traversal by the pointer to the least significant byte on the right before it can perform the addition.
Extras
This is a function in C++ to find out whether our computer is Big-endian. The JVM is using Big-endian under the hood.
bool is_big_endian(void)
{
union {
uint32_t i;
char c[4];
} bint = {0x01020304};
return bint.c[0] == 1;
}